Maps
Browse through maps depicting Bay health and restoration, including pollution trends, public access sites and more.
Chesapeake Bay 2003 Segmentation Scheme - Codes
Date created: January 27, 2008The 2003 Chesapeake Bay Program Segmentation Scheme is a revision of the 2000 version that incorporates four changes: the addition of a new segment (ANATF) that separates the Anacostia River from the rest of the Potomac Tidal Fresh (POTTF) segment, the merger of two Elizabeth River segments (ELIMH and ELIPH into ELIPH) and the small segment boundary location changes between Mattaponi River segments MPNTF and MPNOH and between Choptank River segments CHOTF and CHOOH. Further information about the 2003 Chesapeake Bay Program Segmentation Scheme can be found at http://www.chesapeakebay.net/segmentscheme.htm
View map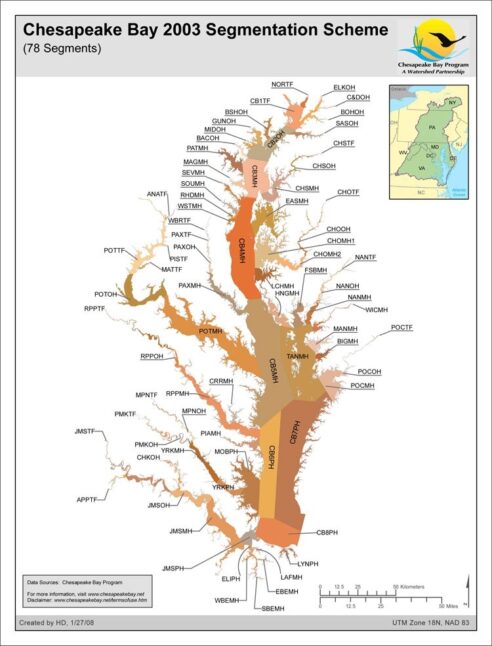
Prime Farmland - Resource Lands Assessment
Date created: January 24, 2008Assessing the extent of farming on prime soils in the Bay watershed is a useful measure for determining the lands of highest importance for agricultural productivity and sustainability. This map shows the acres of potential prime soils that are actively farmed per square mile grid cell.
View map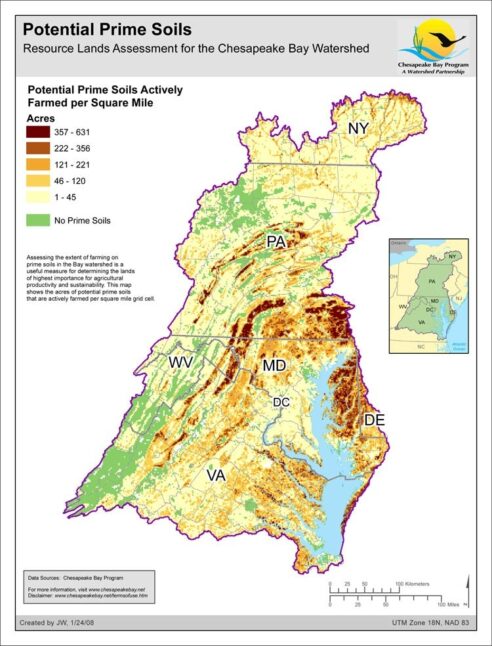
Water Quality Protection Value - Resource Lands Assessment
Date created: January 24, 2008The Water Quality model aims to identify forests and wetlands important in protecting water quality and sustaining watershed integrity. This "watershed value" is based on physical and biological functions that store precipitation, retain and assimilate nutrients, moderate runoff, protect soils and maintain important critical landscape functions such as those of riparian buffers.
View map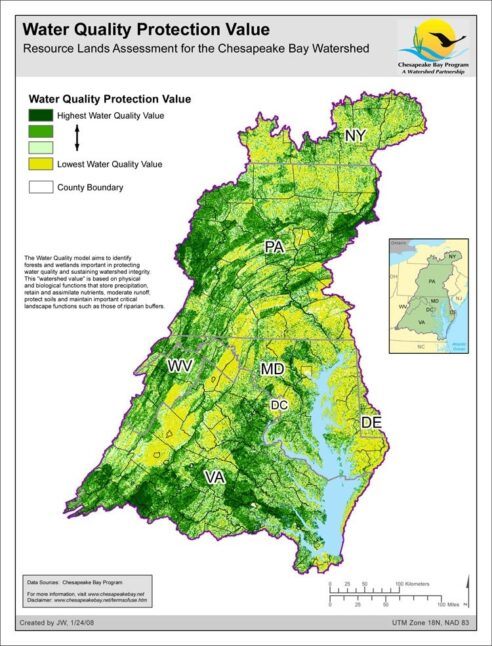
Vulnerability - Resource Lands Assessment
Date created: January 23, 2008The Resource Lands Assessment vulnerability layer evaluates the relative potential risk of future land conversion to urban uses. Vulnerability is defined as a function of suitability for development and proximity to growth "hot spots". The vulnerability layer is useful as a stand-alone layer to evaluate development trends, but can also be combined with the other RLA layers to prioritize land conservation efforts.
View map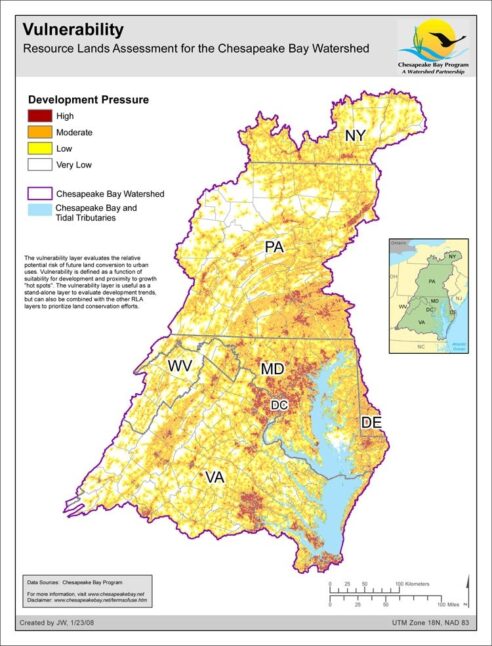
Ecological Network - Resource Lands Assessment
Date created: January 23, 2008The Ecological Network Assessment aims to identify the most important remaining habitats in the Virginia, Maryland, Pennsylvania, West Virginia, Delaware, and D.C. portions of the Bay Watershed. The assessment applies a "hubs and corridors" approach, which is based on principles of landscape ecology and conservation biology, that suggest that size and connectivity are critical factors of high integrity habitat.
View map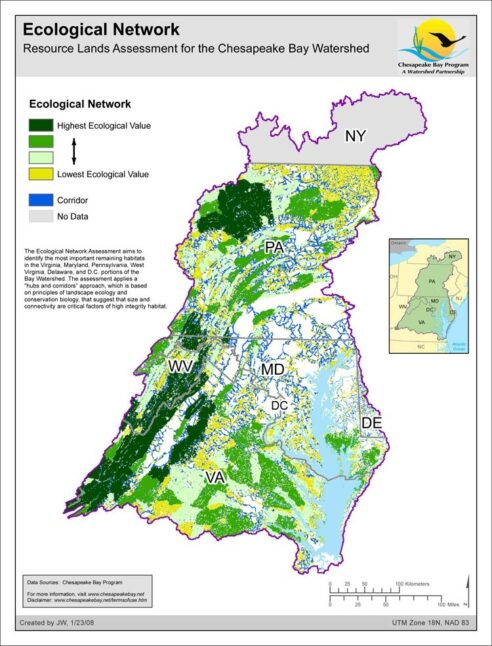
Land Cover: Chesapeake Bay Watershed
Date created: January 23, 2008The National Land Cover Database 2001 land cover layer for mapping zone 60 was produced through a cooperative project conducted by the Multi-Resolution Land Characteristics (MRLC) Consortium, a partnership of federal agencies (www.mrlc.gov), consisting of the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), the U.S. Forest Service (USFS), the National Park Service (NPS), the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS), the Bureau of Land Management (BLM) and the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS). It is intended to serve as a consistent, seamless, and accurate National Land Cover Database circa 2001 for the US at medium spatial resolution. The NLCD 2001 is created by partitioning the U.S. into 66 mapping zones delineated within the conterminous U.S. based on ecoregion and geographical characteristics, edge matching features and the size requirement of Landsat mosaics. The Chesapeake Bay Watershed is derived from zone 60 which encompasses whole or portions of several states, including the states of New York, Delaware, Maryland, Pennsylvania, Virginia, and the District of Columbia. The Chesapeake Bay Program GIS Team modified this data to represent low/medium intensity development, high intensity development, wetlands, forest, agriculture, and barren land within the Chesapeake Bay Watershed.
View map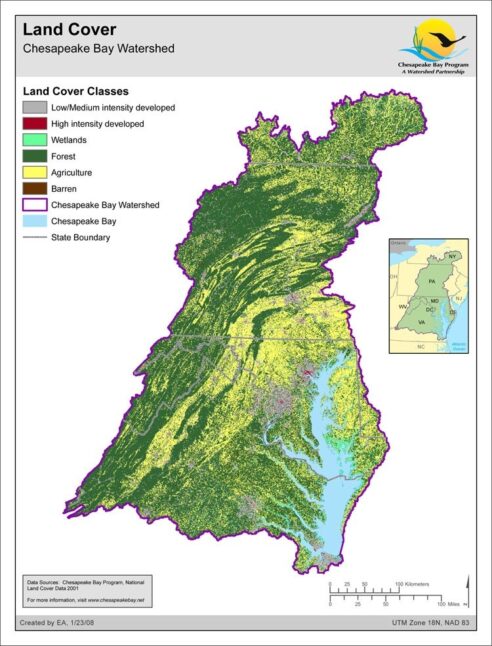
Forest Economics - Resource Lands Assessment
Date created: January 23, 2008The identification of economically important forest lands focuses on the potential for future economic benefits associated with timber management activities. This considers not only the potential economic gain from forest harvest operations, but also the long-term economic sustainability of forest management and the local importance of the timber and wood products industry.
View map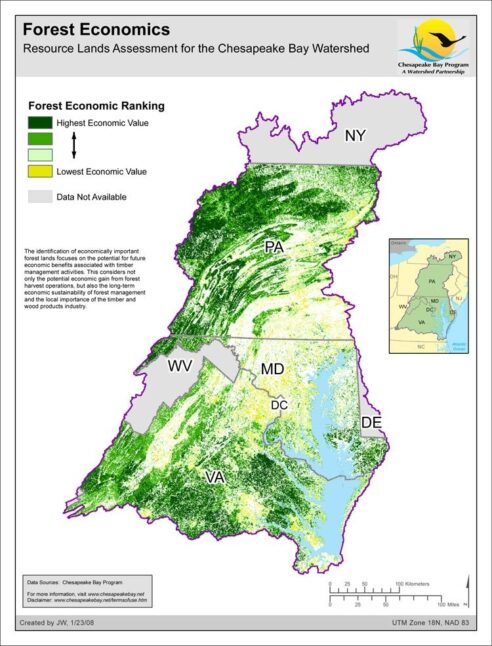
Phase 5.0 Model Segmentation, Chesapeake Bay Watershed Model
Date created: January 17, 2008In order to divide the model domain into county based land segments, a finer segmented river reach network and associated watersheds.This data set is an ArcGIS shapefile depicting land segments in the Chesapeake Bay Watershed and adjacent states of New York, Pennsylvania, Maryland, West Virginia, Delaware, Virginia as well as North Carolina and Tennessee (not shown). Land segmentation was based on county boundaries represented by a 1:100,000-scale digital dataset. Fifty of the 254 counties and incorporated cities in the model region were divided on the basis of physiography and topography, producing a total of 310 land segments. The data are projected to the UTM grid coordinate system - Zone 18 NAD83. Land and watersheds segments were intersected to create land-watershed segments for the model. The land segments are to be used with the Chesapeake Bay Regional Watershed Model to represent the county political boundaries and areas of differing physiography and topography in the study area.
View map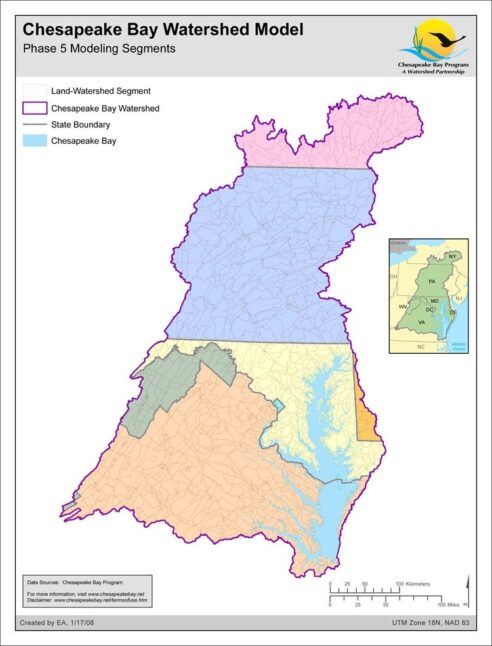
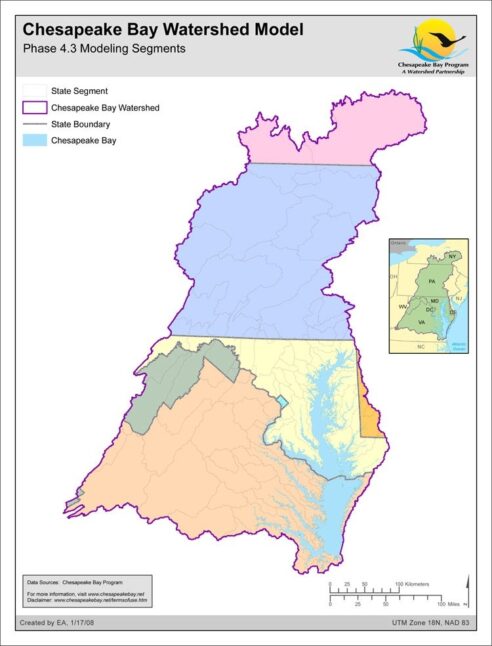
Chesapeake Bay Watershed Model: Phase 4.3 Modeling Segments
Date created: January 17, 2008Final 2003 Phase 4.3 Chesapeake Bay Watershed Model Segments. The intersection of counties found in the study are roughly 8-digit HUC sized watersheds used in conjunction with the HSPF based Phase 4.3 Chesapeake Bay Watershed Model for simulation of nutrient and sediment delivery to the tidal waters of the Chesapeake Bay.
View map